GPL: Generative Pseudo Labeling for Unsupervised Domain Adaptation
Type: Paper
Introduction
-
What is the name of the GPL paper?
GPL: Generative Pseudo Labeling for Unsupervised Domain Adaptation of Dense Retrieval
Kexin Wang, Nandan Thakur, Nils Reimers, Iryna Gurevych
- What are the main contributions of the GPL paper?
- GPL technique for unsupervised domain adaptation
- outperform other methods on 6 datasets
- explore different pretraining approaches
- One problem with dense neural retrieval methods is that they do not
generalize well out of domain- for example, models trained on MS-MARCO perform poorly on task related to COVID-19
- What are some pretraining tasks for dense retrievers?
- In domain continued pretraining
- Inverse cloze task
- ConDensor
- SIMCSE
- Contrastive Tension
- CT
- TSDAE
- Contrastive Tension (CT) (Carlsson et al.,
2021) passes the input through two different models
- similar to original Assymetric encoder from DPR
- ConDensor
(CD) (Gao and Callan, 2021) applies MLM on top
of the CLS token embedding from the final layer
and the other
context embeddings from a previous layer- aim is to force the model to learn meaningful CLS representation.
- MoDIR to use
Domain Adversarial Training(DAT) (Ganin et al., 2016) for unsupervised domain adaptation of dense retrievers.- MoDIR trains models by generating domain invariant representations to attack a domain classifier.
- Seems similar to Pavlos Adversarial Variational Domain Adaptive pretraining paper
- Might mess up the embedding space by forcing different domains to align
- Reseach shows that cross encoders for dense retrieval are more
robust to domain shifts- however due to efficiency reasons application is limited to a reranking step
- One way to leverage cross encoders for efficient retrieval is to
use them to train biencoders
Method
-
The GPL method consists of a
query generation step, negative mining using dense retrieval and pseudolabeling with a cross encoder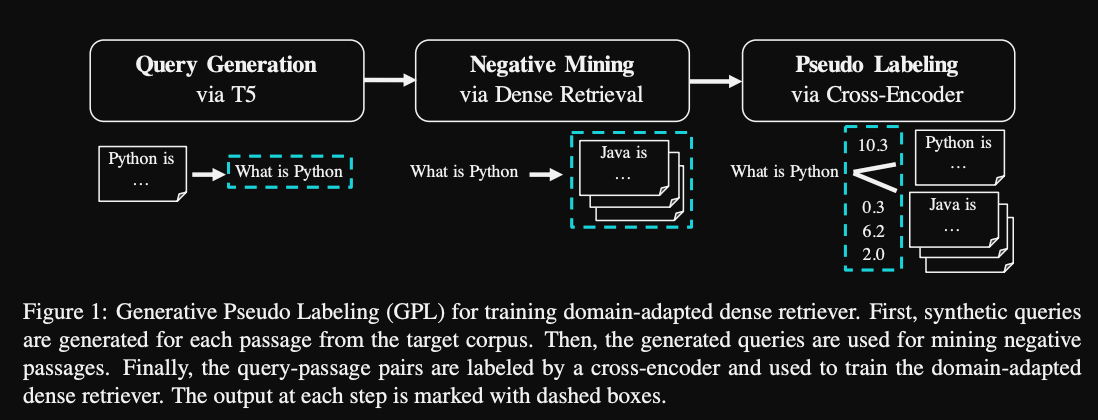
- To work GPL simply needs
paragraphs of in domain text - GPL performs query generation using
T5- generate 3 queries for each in domain passage
- GPL generates negative samples by using
an existing dense retriever- we have generated queries and retrieve the 50 nearest passages
- GPL generates pseudolabels using a
cross encoder- margin is computed between positive instance and negative sample
- these margin scores are saved as pseudolabels
- In GPL, the margin MSE loss trains the biencoder to
mimic the margin predicted by the cross encoder- provides robustness to badly generated queries
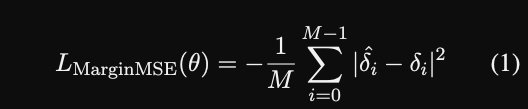
- GPL biencoder model is
distilBERT with mean pooling- use DocT5Query for query generation
- use msmarco-MiniLML-6-v as dense retriever
- use ms-marco-MiniLM-L6 as cross encoder
Results
-
GPL results: gets best performance combined with
TSDAE pretraining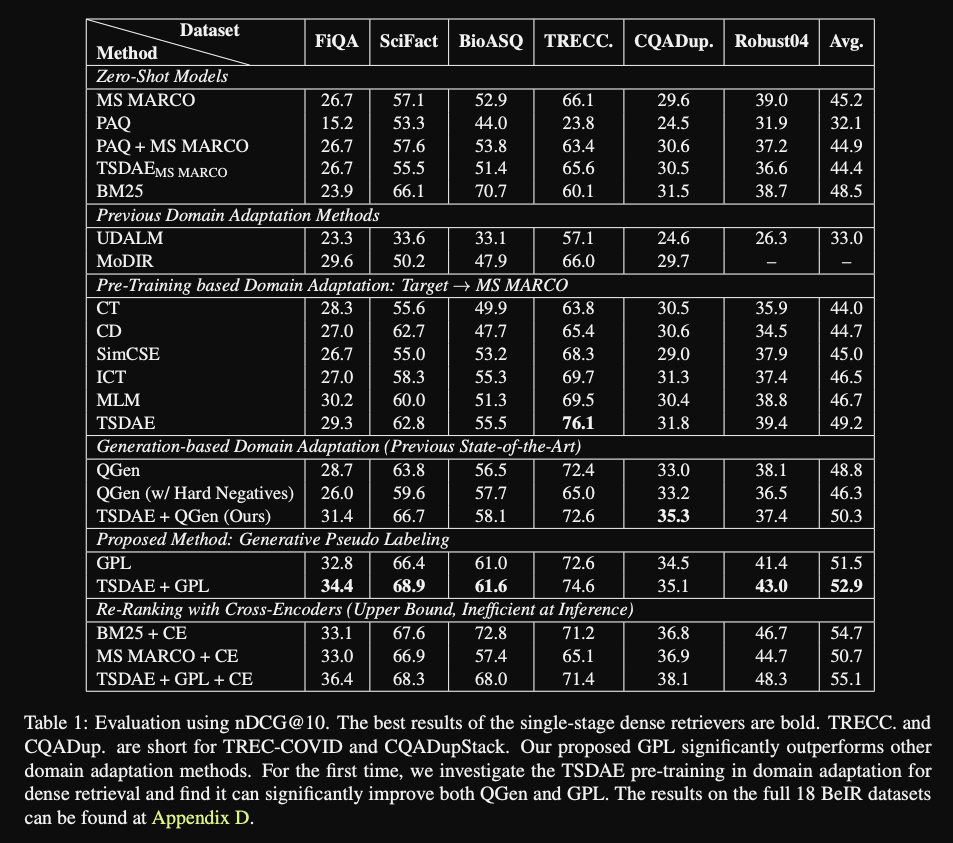
-
GPL training curve, needs about
100ktraining steps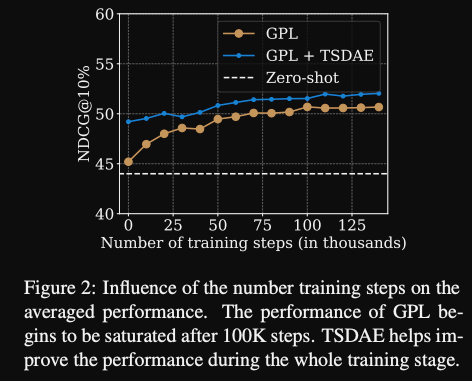
-
One advantage of the GPL method is the
fine-grained cross-encoder scores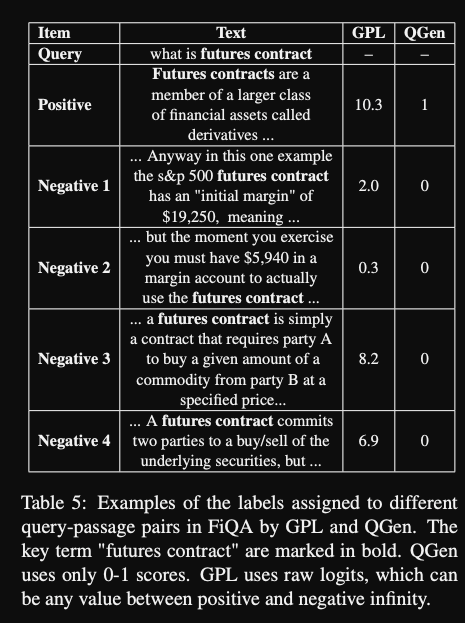
Conclusions
It would be nice to see benchmarks compared to models with larger hidden sizes as many practical use cases don’t necessarily need to trade off performance for the smaller size of distilBERT.
Reference
@article{Wang2021GPLGP,
title={GPL: Generative Pseudo Labeling for Unsupervised Domain Adaptation of Dense Retrieval},
author={Kexin Wang and Nandan Thakur and Nils Reimers and Iryna Gurevych},
journal={ArXiv},
year={2021},
volume={abs/2112.07577}
}
